We are ready for Science 5th
domingo, 1 de octubre de 2017
sábado, 30 de septiembre de 2017
martes, 26 de septiembre de 2017
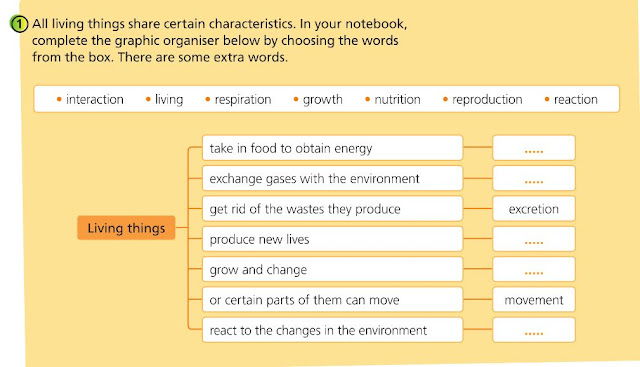
Characteristics of living things.
Characteristics of living things:
NUTRITION
RESPIRATION
EXCRETION
REPRODUCTION
GROWTH
MOVEMENT
INTERACTION
- NUTRITION
- RESPIRATION
- EXCRETION
- REPRODUCTION
- GROWTH
- MOVEMENT
- INTERACTION
Nutrition
Living things take in food to obtain energy.
Respiration
Living things exchange gases with the envoronment.
Excretion
Living things get rid of the wastes they produce.
Reproduction
Living things produce new lives.
Growth
Living things grow and change.
Movement
Living things or certain parts of them can move.
Interaction
Living things react to the changes in the environment.
lunes, 25 de septiembre de 2017
2. Five living things and five non-living things.
What differences can you find between the two charts?
-Living things are born, -Non-living things don't need
they grow, air and food like me and you.
they reproduce and They can be:
they die. -natural or
They need oxygen, food -man-made.
and water to live.
3. Name the life forms in each photo.
Do you know which kingdom they belong to?
LIFE FORMS: jellyfish, toadstool and bacteria.
KINGDOMS THEY BELONG TO:
-A jellyfish is an invertebrate animal.
-The toadstool is a fungus.
-Bacteria belong to a kingdom called Monera.
4. Look at the words below.
Do you think these things are living or non-living?
mould =moho....................living thing.
seed=semilla......................seed is a dormant living.
water=agua........................non-living.
mineral=mineral................mineral.
moss=musgo......................living.
spider=araña.......................living.
MOULD

SEED
sábado, 23 de septiembre de 2017
Review. Unit 1. PB, page 17.
https://www.slideshare.net/AnaCrisGota/unit-1-living-things-53453856

a. Fungi can't make their own food.
b. Algae belong to the Protist Kingdom.
d. Yeasts are unicellular fungi.
e. Algae can make their own food.

f. Viruses aren't considered living things.
a. Chloroplasts. They contain chlorophyll and
only plant cells have them.
b. Cell membrane. It controls what enters and
leaves the cell.
c. Nucleus. It controls all the functions of the cell.
d. Cytoplasm. Most chemical reactions take place
here.
e. Cell wall. They give cell plants their shapes.
a. The small units that make up living ghings are
called CELLS.
b. MICROSCOPES are scientific instruments
that allow us to see cells.
c. The organisms made up of many cells are called
MULTICELLULAR organisms.
d. DICHOTOMOUS keys are used to identify and
classify organisms.
How are living things classified?
HOW ARE LIVING THINGS CLASSIFIED?
LIVING THINGS ARE CLASSIFIED
INTO FIVE GROUPS CALLED KINGDOMS.
They have been grouped this way
because
organisms of the same kingdom:
-----share similarities and
-----are different from organisms in other kingdoms.
PLANT KINGDOM
a. Plants are multicellular.
b. They make their own food through a process called
photosynthesis.
c. Examples: trees, cactus,
PROTIST KINGDOM
a. Protists are usually unicellular, but some are multicellular.
b. Most protists are found in water.
c. Examples: amoeba (unicellular)
algae (algae can be unicellular or multicellular)
Are algae plants?
What kingdom do they belong to?
kelp
MONERA KINGDOM
a. All organisms are unicellular.
b. They can be found on land, in the air, in water and
inside other living things.
c. Example: bacteria.
ANIMAL KINGDOM
a. Animals are multicellular.
b. They get the energy they need by feeding on other living
things.
c. Examples: lion, octopus, spider, fish, bird....
FUNGUS KINGDOM
a. Fungus can be unicellular or multicellular.
b. They obtain the nutrients they need from the remain of
dead plants and animals.
c. Examples: Yeasts are unicellular fungi.
Mushrooms are multicellular fungi.
VIRUSES ARE MICROSCOPIC
AND CAN CAUSE DISEASE.
Most scientist don't consider viruses living things
because they don't take in nutrients,
they produce no waste products,
they don't grow, and
they don't respond to stimuli.
In order to reproduce they must always be
inside another living thing.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)